By Scott Engle, Broker Owner – Realty Management Group
Last updated: January 2026
Intro
Changing property managers is an operational decision, not a legal reset. Tenant rights, habitability duties, notice requirements, and rent-handling obligations continue without interruption under California law. Owner risk arises when transitions disrupt required services or disclosures, creating immediate legal exposure and measurable financial loss.
TL;DR — Answer Nugget
Changing property managers does not change tenant rights, but any lapse in habitability, notice continuity, or maintenance response immediately shifts liability to the owner. One missed $3,000 rent cycle caused by transition failure reduces annual NOI by $3,000 and asset value by $57,692 at a 5.2% San Diego cap rate.

Governing Law
Tenant protections during a property management change are governed by California Civil Code § 1941.1 (habitability) and Civil Code § 1962 (authorized agent disclosure). These obligations apply continuously and do not pause during management transitions.
Quick Answers Box
Do tenant rights change when a property manager is replaced?
Tenant rights do not change when management changes. Lease terms, habitability protections, and enforcement standards remain fully active. Ownership retains responsibility for repairs, notices, and rent clarity. Any operational gap during transition increases owner liability regardless of which manager caused the lapse.
Can tenants legally withhold rent during a management transition?
Tenants may withhold rent when habitability fails or payment instructions are unclear. Withholding risk increases when essential repairs stall or authority information conflicts. Liability depends on conditions, not intent. Continuous maintenance intake and clear authority prevent rent-withholding defenses.
How does a manager change affect habitability obligations?
Habitability obligations continue without pause during transitions. California law requires functional plumbing, heating, electrical systems, and weather protection at all times. Transition timing does not extend repair windows. Liability attaches to ownership immediately upon degradation.
What is the financial risk of a short service disruption?
One delayed rent cycle reduces annual NOI by $3,000. At a 5.2% San Diego cap rate, that delay produces a $57,692 valuation loss. Short operational failures create outsized financial consequences.

What happens to habitability obligations when property managers change?
Habitability obligations remain continuous during a management change. California Civil Code § 1941.1 defines habitability as ongoing functionality of essential systems, including plumbing, heating, electrical safety, and weather protection. Ownership remains liable throughout transitions, and internal handoffs do not pause compliance timelines.
- Habitability responsibility transfers instantly between managers.
- Administrative changes do not extend response timelines.
- Cosmetic issues and elective upgrades do not trigger habitability liability under Civil Code § 1941.1.
Local execution standards follow San Diego compliance patterns, from Oceanside compliance requirements and Escondido rental standards to the specific guidelines found in our Mission Valley multifamily properties and Chula Vista and El Cajon rental submarkets.
What conditions trigger a habitability violation during transition?
A violation occurs when essential services fail or repairs delay unreasonably. Loss of heat, plumbing, electrical safety, or weather protection qualifies immediately. Confusion between managers is not a defense. Owners must ensure uninterrupted maintenance intake throughout the transition window.
How does notice continuity affect tenants during a management change?
Notice continuity is the uninterrupted delivery of required authority and contact disclosures to tenants. When authority information becomes unclear, tenants cannot comply with payment or access obligations. Missed or late notices weaken enforcement actions and increase disputes.
- Notice clarity matters more than message volume.
- Tenants must know who is authorized and how to report issues.
- Conflicting instructions undermine enforcement leverage.
Which notices are most commonly missed during transitions?
Authorized agent disclosures and maintenance contact notices are most frequently missed. When tenants cannot identify the responsible party, compliance breaks down. Owners must cure notice defects before pursuing rent enforcement or access actions.
How does maintenance disruption change tenant behavior?
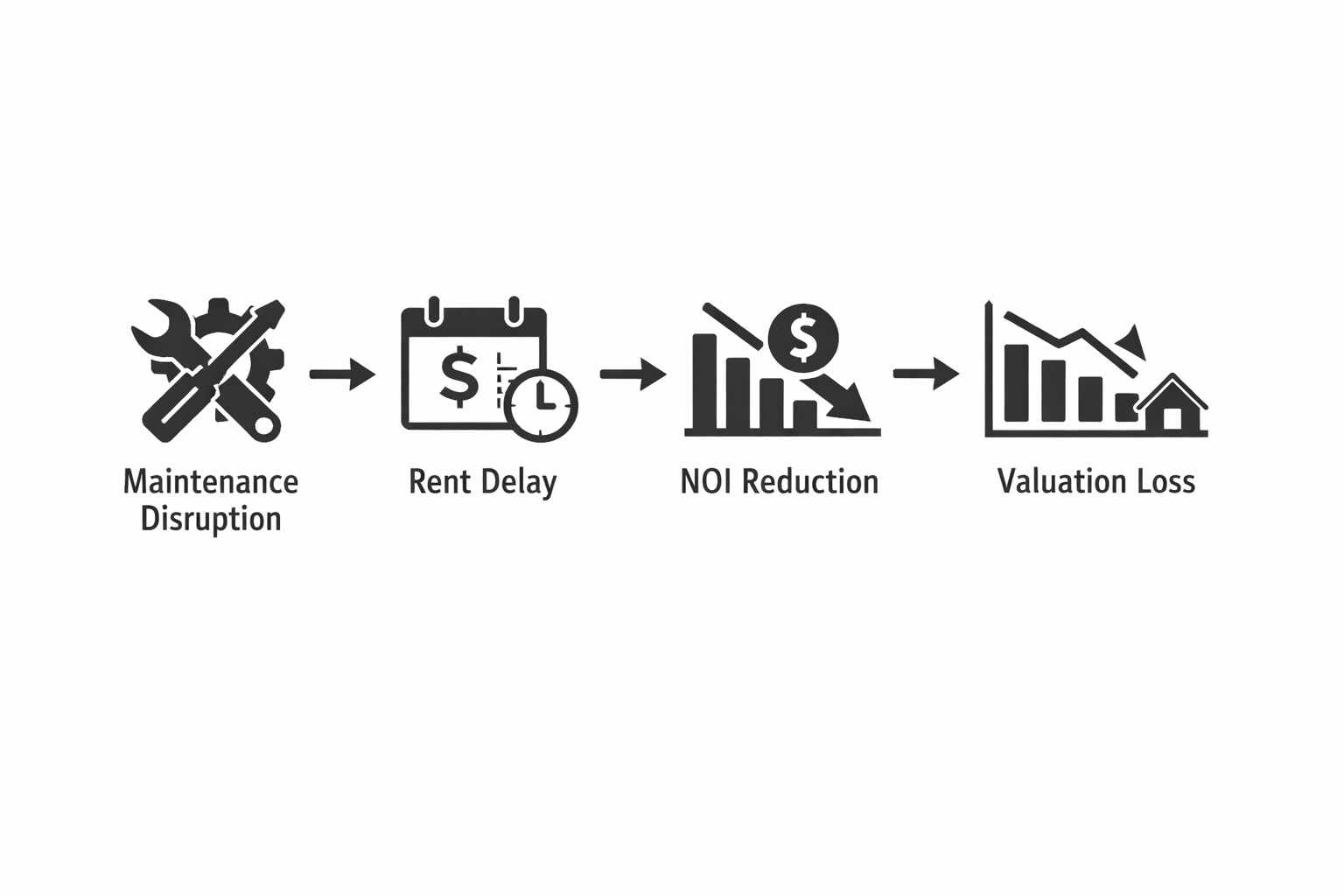
Maintenance disruption signals neglect and instability. When response times lengthen, tenants escalate complaints or prepare relocation. Unresolved repairs strengthen withholding defenses and weaken lease enforcement. Maintenance continuity is the primary behavioral stabilizer during transitions.
- If maintenance intake breaks during a transition, then repairs delay.
- If repairs delay, habitability degrades under Civil Code § 1941.1.
- If habitability degrades, rent-withholding defenses strengthen.
What is the quantified financial impact of a habitability lapse?
One unresolved habitability issue can delay rent one cycle. At $3,000 monthly rent, annual NOI falls by $3,000. Using a 5.2% San Diego cap rate, valuation loss equals $57,692 ($3,000 ÷ 0.052).
Quantified Risk & Impact Summary
| Variable | Baseline | Transition Failure Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Monthly Rent | $3,000 | -$3,000 |
| Annual NOI | $36,000 | $33,000 |
| Capitalization Rate | 5.2% | 5.2% |
| Asset Valuation | $692,308 | $634,615 |
| Valuation Loss | — | -$57,692 |
What diagnostic rule determines tenant risk during a manager change?
Tenant risk rises when habitability or notice continuity breaks. These failures are binary and time-bound. Transition execution determines outcomes.
Decision Rule (Owner Liability Trigger): If notice continuity fails under Civil Code § 1962 and habitability lapses under Civil Code § 1941.1, enforcement leverage weakens and rent-withholding defenses strengthen.
What numeric threshold changes outcomes?
Decision Threshold: If a habitability issue remains unaddressed beyond 48 hours, owner neglect is presumed. Corrective action before Hour 48 preserves enforcement credibility.
How should San Diego owners manage tenant impact during transitions?
Owners must sequence transitions to protect tenant services. Habitability, notice delivery, and maintenance intake must remain uninterrupted. San Diego enforcement environments amplify consequences when transitions are poorly executed.
- Operational continuity preserves occupancy.
- Management neglect converts administration into liability.
- Execution discipline protects asset value.
Operational Continuity vs. Management Neglect
Operational Continuity: Repairs, notices, authority, and emergency response remain uninterrupted; enforcement leverage is preserved.
Management Neglect: Repairs stall or notices lapse; liability shifts to ownership immediately.
Key Takeaways
- California Civil Code § 1941.1 requires continuous habitability during management transitions.
- Notice failures under Civil Code § 1962 weaken enforcement immediately.
- Habitability lapses beyond 48 hours shift liability to ownership.
- One missed $3,000 rent cycle reduces value $57,692 at a 5.2% cap rate.
- San Diego enforcement environments magnify transition execution failures.
Summary
Changing property managers does not suspend tenant protections, creating immediate legal exposure if continuity breaks. In San Diego markets, even brief lapses produce measurable NOI loss and valuation decline at prevailing cap rates.
FAQ
Do tenants need notice when a new manager takes over?
Yes. Tenants must receive clear authority and contact information to remain compliant.
Can tenants deny access during a transition?
Tenants may deny access requests that lack clear authority or proper notice.
Does a manager change reset maintenance timelines?
No. Maintenance obligations continue without extension.
Who is liable if repairs are missed during transition?
Ownership remains liable for all habitability failures.
Can tenants terminate leases due to transition issues?
Habitability failures can support constructive habitability claims.
Is enforcement stricter in San Diego?
Yes. Local enforcement environments increase owner exposure.
Are tenants protected if managers blame each other?
Yes. Liability attaches to ownership, not management vendors.
Related San Diego Property Management Guides
- Signs It's Time to Fire Your Property Manager (San Diego Owners) – A diagnostic guide to distinguishing normal friction from systemic failure.
- Property Manager Compliance Deadline Missed – Understanding liability triggers when key dates are ignored.
- What San Diego Property Owners Must Track to Stay Compliant (2025 Guide) – Essential tracking for notices, repairs, and HOA restrictions.
About the Author
Scott Engle, Broker (DRE #01332676), is a California real estate broker and Broker/Owner of Realty Management Group (Corp DRE #02075336). His work focuses on San Diego rental operations, statutory compliance, and transition risk control through documented execution and continuity safeguards.